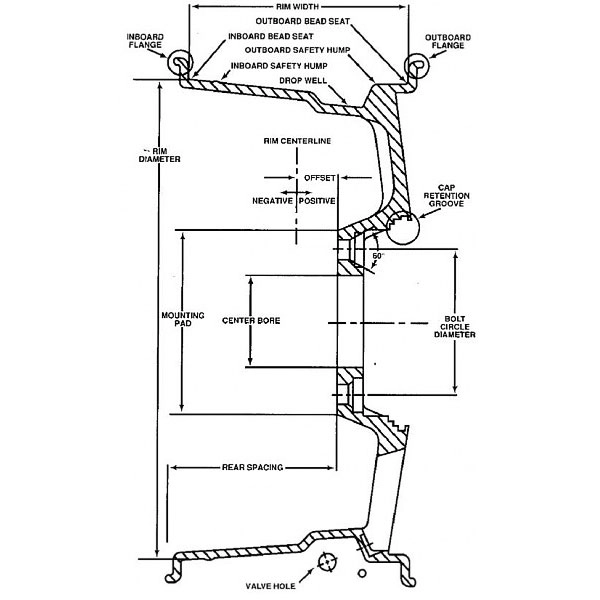
OFFSET / ET
Wheel offset is simply the distance between the wheel’s hub-mounting surface and its center plane. Positive offset means the hub-mounting surface is closer to the wheel’s outboard side. Conversely, negative offset means it’s closer to the inboard side.
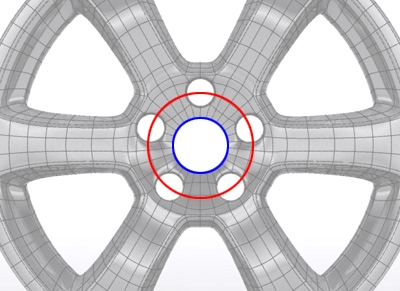
PCD
The most important element of wheel manufacture is the bolt pattern or ‘PCD’ (pitch circle diameter) of the wheel. The bolt pattern of the wheel must mirror the bolt pattern of the vehicle to ensure the wheel nut or bolt seats align and mate across the seating surface of the nut or bolt seats in the wheel.
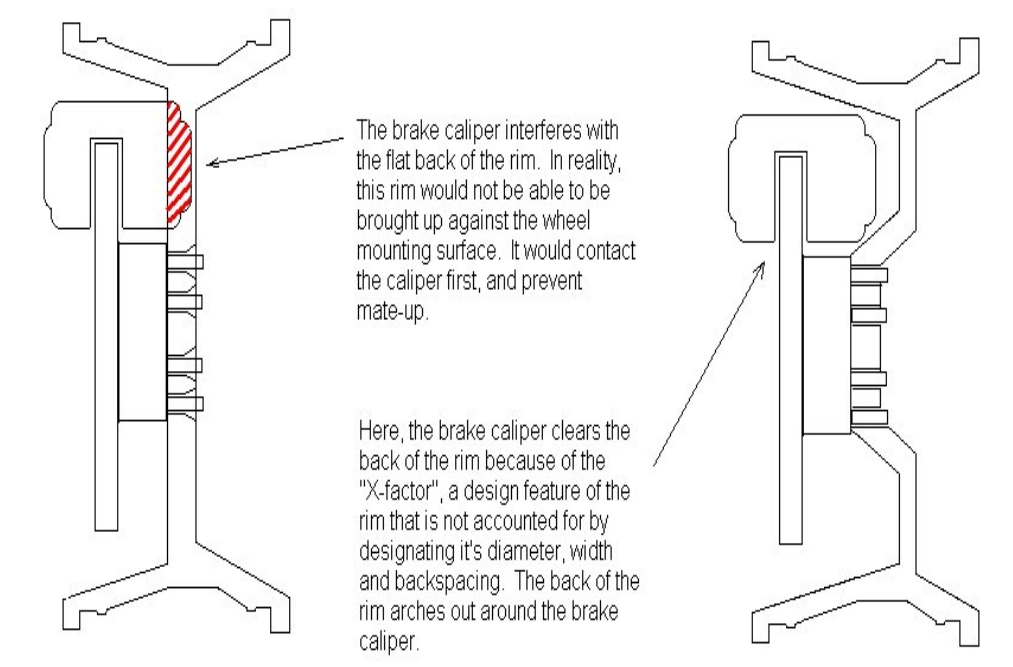
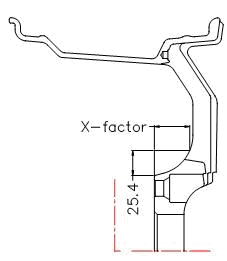
X-FACTOR
X-factor, also called the “The caliper clearance”, is the amount of clearance built into the wheel to clear the vehicle’s caliper assembly.
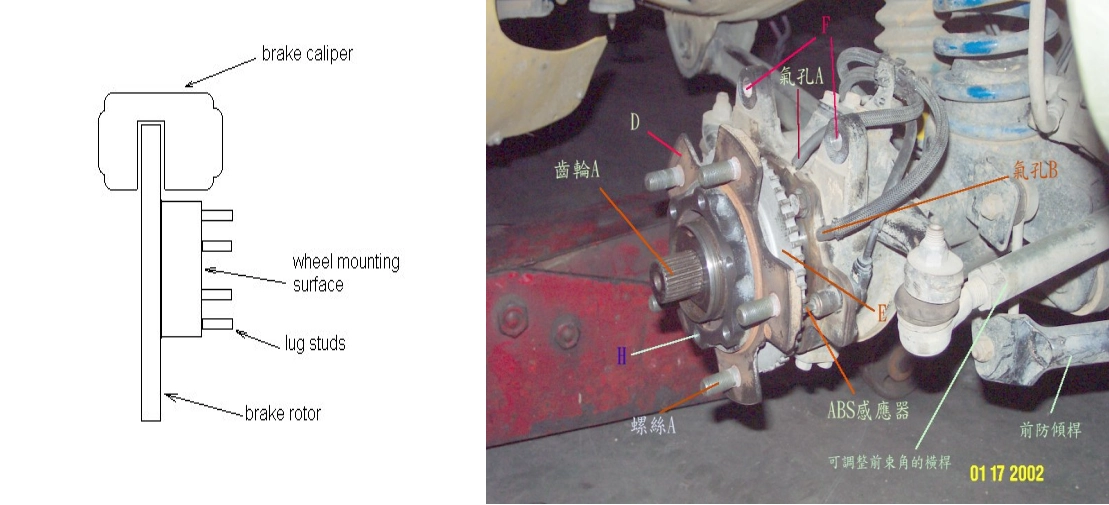
HUB HOLE / CB
The centre bore is the size of the hole in the centre of the wheel where the spigot fits through. The centre bore, (also known as spigot size), is the diameter of this hole, usually measured in millimetres.it’s different for different vehicles, for example, normally CB for BENZ is 66.6mm, and CB for BMW is 72.6mm. If wheel CB is too big, then Center Ring will be necessary to be used to avoid shaking when driving on the high way.
For most road wheels, the weight of the car is transmitted from the spigot, (the bit the centre of the wheel that protrudes from the hub), to the centre hole in the wheel. The job of the wheel studs or wheel bolts is to hold the wheel in place over the spigot. It is therefore very important that the centre bore of the wheel matches the spigot size of the car’s hub.
WHEEL SIZE
The wheel size is the size designation of a wheel given by its diameter, width, and offset.
The diameter of the wheel is the diameter of the cylindrical surface on which the tire bead rides. The width is the inside distance between the bead seat faces. The offset is the distance from the wheel’s true centerline (half the width) to the wheel’s mounting surface. Offset is covered in more detail below. A typical wheel size will be listed beginning with the diameter, then the width, and lastly the offset (+ or – for positive or negative). Although wheel sizes are marketed with measurements in inches, the Michelin TRX introduced in 1975 was marketed in millimeters.
For example, 17 × 8.5 × +35 designates a diameter of 17 inches, width of 8.5 inches, and +35 mm positive offset (432 × 216 × +35 in fully metric numbers).
Replacing the wheels on a car with larger ones can involve using tires with a lower profile. This is done to keep the overall diameter of the tire the same as stock to ensure the same clearances are achieved. Larger wheels are typically desired for their appearance but could also offer more space for brake components. This can come at cost of performance though as larger wheels can weigh more.
Alternatively, smaller wheels are chosen to fit a specific style of vehicle. An example of this is the Lowrider Culture in which smaller wheels are largely desired.
Wheels can be widened to allow for a wider tire to be used and to poke the wheel out to the fender of the vehicle. Running a wider tire allows for more of the vehicle’s power to be put to the ground because there is a larger surface area making contact with the road. This will improve a vehicle’s performance when it comes to acceleration, handling, and braking.
Load capacity:
Load capacity is the amount of mass a wheel will carry. This number will vary depending on the number of lugs, the PCD, the material used and the type of axle the wheel is used on. A wheel used on a free rolling trailer axle will carry more weight than that same wheel used on the drive or steering axle of a vehicle. All wheels will have the load capacity stamped on the back of the wheel. The Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) is the maximum operating mass of a vehicle as specified by the manufacturer. In the United States this information is required to be on the vehicle’s door placard. The load capacity of the total number of wheels on the vehicle combined must meet or exceed the vehicle’s gross vehicle weight rating
Wheel Test
Wheel testing involves a series of tests that are carried out to meet vehicle OEM requirements or the specifications of test standards on bending fatigue, radial fatigue, biaxial impact, energy absorption, radial impact or torsion.
- We’ve developed to a diversified wheel production group. Our factory has passed IATF 16949 System.
- CONTACT DETAILS
Contact: Elias Qin Tel: +86 13736022077 Email:sales@brsautoparts.comAddress: Headquarter 1st, Rili Middle Road, Yinzhou District, Ningbo City, China - CONTACT US


